Biometrics: Making the World More Secure
In today's rapidly evolving world, security is more important than ever. With the rise of technology and the increasing sophistication of threats, traditional security measures are often inadequate. This is where biometric technology comes into play, revolutionizing the way we approach safety. Biometrics refers to the unique physical and behavioral characteristics of individuals, which can be measured and analyzed to enhance security protocols. Imagine a world where your identity is confirmed by your own traits, rather than passwords or security codes that can be forgotten or hacked. This article explores how biometrics is making the world a safer place across various sectors, its numerous benefits, the challenges it faces, and the exciting future trends that promise to further enhance safety and privacy.
At its core, biometrics is all about using unique attributes to identify individuals. This can mean anything from your fingerprints to the way you walk. The fundamental idea is that these traits are inherently yours, making them incredibly difficult to replicate or steal. Biometric systems analyze these characteristics, creating a reliable method for authentication. The technology has evolved significantly over the years, and today, we see various types of biometric systems in use, each tailored for specific applications. Whether it’s for securing your smartphone or monitoring access to sensitive areas, understanding the different biometric modalities is crucial in recognizing their potential in enhancing security.
There are several types of biometric systems, each with its own unique functionalities and applications. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most prevalent forms:
- Fingerprint Recognition: One of the oldest and most widely used biometric technologies.
- Facial Recognition: Gaining traction due to its non-intrusive nature.
- Iris Scanning: Known for its accuracy and reliability.
- Voice Recognition: Utilizes vocal patterns for identification.
Each of these systems has its own set of advantages and challenges, which we will explore in detail in the following sections.
Fingerprint recognition is perhaps the most familiar biometric technology to the average person. It works by capturing the unique patterns of ridges and valleys on an individual's fingertips. When you place your finger on a scanner, the device records the fingerprint and compares it to a stored template. This method is not only quick but also highly accurate, making it a popular choice for various applications.
One of the key benefits of fingerprint technology is its high accuracy. Unlike traditional passwords, fingerprints are unique to each individual, reducing the chances of unauthorized access. Additionally, the technology is user-friendly; most people are familiar with the process of scanning their fingerprints. This has led to its widespread adoption in various environments, including:
- Smartphones and tablets for unlocking devices.
- Secure facilities for access control.
- Financial institutions for authorizing transactions.
Despite its effectiveness, fingerprint recognition is not without its challenges. Issues such as false positives—where the system mistakenly identifies an unauthorized user as legitimate—can pose security risks. Additionally, there is a potential for spoofing, where someone could use fake fingerprints to gain access. These challenges necessitate ongoing advancements in technology to ensure that fingerprint recognition remains a secure option.
Facial recognition technology has surged in popularity, particularly in public spaces. This system analyzes facial features and compares them to a database to identify individuals. While it offers a convenient way to enhance security, it also raises ethical considerations regarding privacy. As we navigate this technology, it’s crucial to find a balance between security and the rights of individuals.
Biometric systems have become an integral part of our daily lives. From the moment we unlock our smartphones to the security systems in our workplaces, these technologies enhance both security and convenience. For instance, using a fingerprint or facial recognition to unlock a device is not just secure; it’s also incredibly convenient, allowing users to access their information quickly without the hassle of remembering complex passwords.
Mobile devices have embraced biometric authentication wholeheartedly. Today’s smartphones often come equipped with multiple biometric methods, including fingerprint scanners and facial recognition systems. This shift not only enhances security but also improves user experience. Imagine being able to unlock your phone with just a glance or a touch—it's a game-changer! This technology not only protects personal information but also streamlines access, making our lives easier.
Biometric technologies play a vital role in enhancing public safety. Law enforcement agencies utilize these systems for surveillance and identifying suspects, significantly improving their efficiency. However, this raises important questions about the balance between security and privacy. As we embrace these technologies, it’s essential to ensure that they are used responsibly and ethically, safeguarding individual rights while enhancing community safety.
Q: What are the most common types of biometric systems?
A: The most common types include fingerprint recognition, facial recognition, iris scanning, and voice recognition.
Q: How secure is biometric technology?
A: While biometric technology is generally secure due to the uniqueness of physical traits, challenges such as spoofing and false positives exist, necessitating continuous improvements.
Q: Can biometric data be hacked?
A: Although biometric data is more secure than traditional passwords, it is not completely immune to hacking. Therefore, it is crucial to implement additional security measures.

Understanding Biometrics
Biometrics is a fascinating field that delves into the measurement and statistical analysis of unique physical and behavioral characteristics of individuals. Imagine a world where your identity is not just a password or a PIN, but something that is inherently you—your fingerprint, your face, or even the way you speak. This technology is not just a futuristic concept; it's a reality that enhances security across various sectors, from personal devices to national security.
At its core, biometrics is about creating a unique identifier based on biological traits. This means that instead of relying on something you can forget or lose, like a password, biometrics uses something that is an integral part of you. The fundamental concepts of biometrics can be broken down into two main categories: physiological and behavioral characteristics.
Physiological characteristics refer to the physical attributes of a person, such as:
- Fingerprints: The unique patterns on the tips of your fingers.
- Facial features: The distinct structure of your face.
- Iris patterns: The unique patterns in the colored part of your eye.
On the other hand, behavioral characteristics involve patterns in your behavior, such as:
- Voice recognition: The unique way you speak.
- Keystroke dynamics: The rhythm and speed with which you type.
The beauty of biometric systems lies in their ability to provide a high level of security while being user-friendly. For instance, when you unlock your smartphone with your fingerprint, you’re not just accessing a device; you’re utilizing a technology that’s designed to be both convenient and secure. This duality is what makes biometrics so appealing in today’s digital age.
However, while biometrics offers numerous benefits, it also raises some questions. How secure is your biometric data? What happens if it gets compromised? These concerns are valid, especially in a world where data breaches are becoming increasingly common. As we explore the various types of biometric systems in the following sections, it’s essential to keep these questions in mind.
In summary, understanding biometrics is crucial as it represents a significant leap forward in security technology. By leveraging unique human traits, biometrics not only enhances security measures but also paves the way for a future where our identities are more secure and less susceptible to theft. As we continue this journey into the world of biometrics, we will uncover the various systems that make this technology a cornerstone of modern security.

Types of Biometric Systems
Biometric systems have revolutionized the way we approach security, offering a range of technologies that leverage unique human characteristics for identification and verification. These systems can be broadly categorized into two types: physiological and behavioral biometrics. Physiological biometrics focus on physical traits, while behavioral biometrics analyze patterns in human behavior. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for appreciating the diverse applications and benefits of biometric technology.
Among the most common types of biometric systems, we find fingerprint recognition, facial recognition, iris scanning, and voice recognition. Each of these technologies operates on distinct principles and serves various purposes in enhancing security. For instance, fingerprint recognition captures the unique patterns on an individual’s fingertips, making it a popular choice for access control in both personal devices and secure facilities. On the other hand, facial recognition technology scans and analyzes facial features to identify individuals, which has gained traction in public surveillance and law enforcement.
Fingerprint Recognition is perhaps the most widely recognized biometric technology. It works by capturing the intricate patterns of ridges and valleys on a person's fingertip using a scanner. This data is then converted into a digital template that can be stored and compared against future scans. Its high accuracy and ease of use have made it a staple in various security applications, from smartphones to secure entry systems in buildings.
Facial Recognition, on the other hand, utilizes advanced algorithms to detect and analyze facial features. This technology can identify individuals in real-time from video feeds, making it a powerful tool for surveillance. However, it also raises significant ethical concerns regarding privacy and consent, especially in public spaces where individuals may not be aware they are being monitored.
Iris Scanning is another sophisticated biometric method that examines the unique patterns in the colored part of a person's eye. This technology is known for its high accuracy and is often used in high-security environments, such as airports and government buildings. It requires specialized equipment, which can make it less accessible than fingerprint or facial recognition systems.
Lastly, Voice Recognition analyzes the unique characteristics of an individual's voice, such as pitch, tone, and cadence. This technology is increasingly used in customer service applications, allowing users to authenticate themselves through voice commands. While it offers convenience, it is also susceptible to issues like background noise and voice imitation, which can impact its reliability.
In summary, the variety of biometric systems available today provides numerous options for enhancing security across different sectors. Each type comes with its own set of advantages and challenges, making it essential for organizations to choose the right technology based on their specific needs and the level of security required. As biometric technology continues to evolve, we can expect further innovations that will make these systems even more effective and user-friendly.

Fingerprint Recognition
Fingerprint recognition is a fascinating technology that has become a cornerstone of biometric security systems. Imagine a world where your unique fingerprint is the key to accessing your most sensitive information and secure locations. This technology leverages the distinct patterns found in human fingerprints, making it incredibly reliable and efficient. When you place your finger on a scanner, the device captures the intricate details of your fingerprint, converts them into a digital format, and compares them against stored data to verify your identity. It's like having a personal bodyguard that only lets the right person in!
The applications of fingerprint recognition are vast and varied. From unlocking smartphones to securing entry points in high-security facilities, this technology is everywhere. In fact, many people use it daily without even thinking about it. For instance, when you swipe your finger on your phone to unlock it, you're utilizing a system that has been meticulously designed to keep your data safe. The convenience and speed of fingerprint scanning make it a preferred choice for many users, as it allows for quick access without the need for passwords or PINs.
One of the standout features of fingerprint recognition is its high accuracy. The technology has advanced significantly over the years, reducing the chances of false positives and negatives. Most modern systems can achieve accuracy rates of over 99%, which is impressive! However, like any technology, it’s not without its challenges. For example, environmental factors such as dirt or moisture can affect the scanner's ability to read fingerprints accurately. Additionally, the risk of spoofing—where an unauthorized person uses a fake fingerprint to gain access—remains a concern. To combat this, many systems are now incorporating additional security measures, such as liveness detection, which checks whether the fingerprint is from a real person.
In summary, fingerprint recognition offers a blend of convenience, security, and reliability. As we continue to embrace biometric technologies in our daily lives, understanding how these systems work and their implications for security is essential. The future of fingerprint recognition looks promising, with ongoing advancements aimed at enhancing its accuracy and security features. As we move forward, it’s exciting to think about how this technology will evolve and shape the way we interact with our devices and environments.
- How does fingerprint recognition work? Fingerprint recognition captures the unique patterns of a person's fingerprint and compares them to stored data to verify identity.
- Is fingerprint recognition secure? Yes, it is generally considered secure, but it can be vulnerable to spoofing and environmental factors.
- Can fingerprint scanners be fooled? While they are highly accurate, there are methods to spoof fingerprint scanners, which is why additional security measures are often employed.
- Where is fingerprint recognition used? It is used in various applications, including smartphones, security systems in buildings, and law enforcement.

Advantages of Fingerprint Technology
Fingerprint technology has revolutionized the way we approach security, providing an array of benefits that make it a go-to choice for many applications. One of the most significant advantages is its high accuracy. Unlike traditional password systems that can be forgotten or easily guessed, fingerprint recognition relies on unique biological traits that are nearly impossible to replicate. This inherent uniqueness means that the chances of a false acceptance are incredibly low, making it a reliable method for securing access to sensitive areas.
Moreover, the ease of use associated with fingerprint technology cannot be overstated. Users simply place their finger on a scanner, and within seconds, they gain access to their devices or secure locations. This swift process not only enhances user experience but also streamlines operations in environments where efficiency is crucial, such as airports and corporate offices. Imagine walking into a building without fumbling for your ID or remembering a complex password; that’s the convenience fingerprint technology brings!
Another key advantage is the cost-effectiveness of implementing fingerprint recognition systems. While the initial setup costs may seem daunting, the long-term savings on administrative tasks and the reduction in security breaches can offset these expenses significantly. Organizations no longer need to manage the logistics of issuing and replacing key cards or passwords, which can lead to substantial operational savings over time.
Additionally, fingerprint technology enhances accountability. With traditional security methods, it can be challenging to track who accessed what and when. However, biometric systems create detailed logs of user access, making it easier for organizations to monitor and audit entries. This feature is particularly beneficial in high-security environments such as data centers or laboratories where sensitive information is stored.
To sum it up, the advantages of fingerprint technology include:
- High Accuracy: Minimizes false acceptance and enhances security.
- Ease of Use: Quick and convenient access for users.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces long-term operational costs.
- Accountability: Provides detailed access logs for monitoring.
As we continue to evolve in a world that increasingly values security and convenience, fingerprint technology stands out as a solution that meets both needs effectively. It’s clear that this biometric method is not just a trend but a fundamental shift in how we approach security in our daily lives.

Challenges of Fingerprint Recognition
While fingerprint recognition technology has revolutionized security systems across various sectors, it is not without its challenges. One of the most significant issues is the occurrence of false positives and false negatives. A false positive occurs when the system incorrectly identifies a non-matching fingerprint as a match, while a false negative happens when a matching fingerprint is not recognized. These errors can lead to unauthorized access or, conversely, deny access to legitimate users, creating frustration and potential security risks.
Another challenge is the potential for spoofing. Criminals can create fake fingerprints using materials such as gelatin or silicone, which can trick the biometric systems into granting access. This vulnerability raises concerns about the overall reliability of fingerprint recognition, particularly in high-security environments where the stakes are much higher.
Moreover, the effectiveness of fingerprint recognition can be affected by various factors, including skin conditions, age, and environmental factors. For instance, individuals with dry or damaged skin may find it difficult for the system to accurately read their fingerprints. Similarly, harsh weather conditions or dirty sensors can hinder the performance of the technology, leading to increased failure rates.
Additionally, there are important privacy concerns associated with the collection and storage of fingerprint data. Users often worry about how their biometric information is being used and whether it is adequately protected from data breaches. In a world where cyber threats are increasingly common, the potential for hackers to access and misuse biometric data is a significant concern, making it crucial for companies to implement robust security measures.
Finally, the cost of implementation can also be a barrier for many organizations. High-quality fingerprint recognition systems can be expensive to install and maintain, which may deter smaller businesses from adopting this technology. Balancing the need for security with budget constraints is a challenge that many organizations face.
- What are the most common challenges with fingerprint recognition technology? The most common challenges include false positives and negatives, spoofing, environmental factors affecting performance, privacy concerns, and high implementation costs.
- How can organizations mitigate the risks associated with fingerprint recognition? Organizations can implement multi-factor authentication, regularly update their security systems, and educate users about the importance of protecting their biometric data.
- Is fingerprint recognition technology reliable? While fingerprint recognition is generally reliable, its effectiveness can be influenced by various factors, including skin condition and environmental conditions.
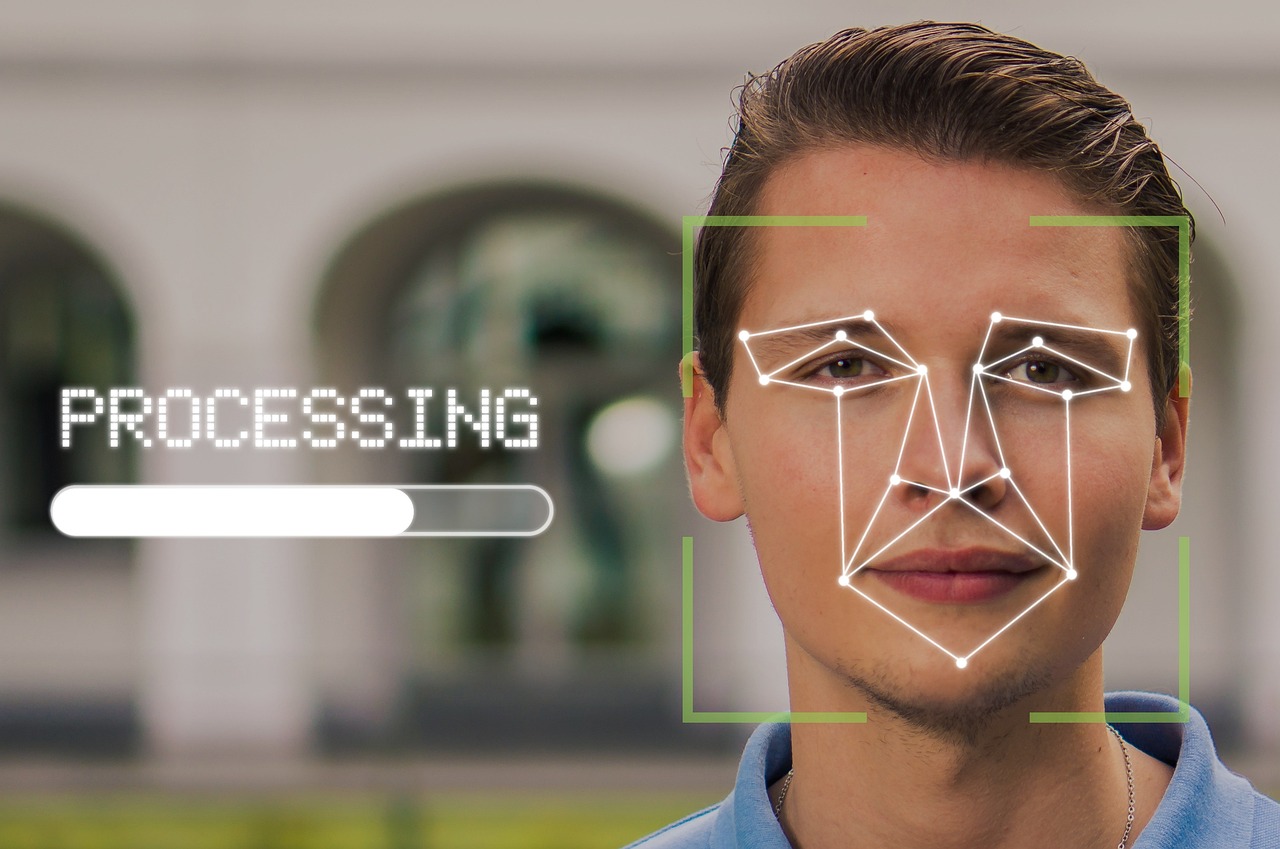
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition technology has rapidly transformed from a futuristic concept into a practical tool that is reshaping how we think about security and personal identification. At its core, this technology utilizes advanced algorithms to analyze facial features and compare them against a database of known faces. Imagine walking into a building and having the door unlock automatically because the system recognizes your face—this is not science fiction; it's the reality of facial recognition today!
One of the most fascinating aspects of facial recognition is its ability to function in real-time. This means that as you approach a camera, the system can instantly capture your image, analyze it, and determine whether you are authorized to enter. This speed and efficiency make it an appealing choice for various applications, from airports to corporate offices. However, while the benefits are substantial, they come with a set of ethical considerations that cannot be ignored.
For instance, the implementation of facial recognition in public spaces raises significant privacy concerns. People often feel uneasy knowing that their movements are being monitored and recorded without their consent. This has sparked a heated debate about the balance between enhanced security and individual privacy rights. Many argue that while facial recognition can help reduce crime rates and enhance safety, it also opens the door to potential misuse and surveillance overreach.
Moreover, the accuracy of facial recognition systems varies depending on several factors, including lighting conditions, angles, and even the demographic characteristics of individuals. Studies have shown that these systems can exhibit biases, often misidentifying people from certain racial or ethnic backgrounds more frequently than others. This inconsistency can lead to serious consequences, such as wrongful accusations or denial of access, which highlights the need for continuous improvement and regulation in the technology's deployment.
As we look to the future, the evolution of facial recognition technology is likely to continue. With advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning, we can expect even more sophisticated systems that not only recognize faces but also interpret emotions or intentions. However, it is crucial that as we embrace these innovations, we also establish robust frameworks to protect individual rights and ensure ethical usage.
In summary, facial recognition technology stands at the intersection of security and privacy. While it offers remarkable benefits in enhancing safety and streamlining processes, it also poses significant challenges that society must address. As we navigate this complex landscape, the dialogue surrounding facial recognition will be essential in shaping a future where technology and ethics coexist harmoniously.
- What is facial recognition technology? Facial recognition technology is a biometric system that identifies or verifies a person by analyzing their facial features and comparing them to a database.
- How does facial recognition work? It works by capturing an image of a person's face, extracting key features, and matching them against stored images in a database.
- What are the benefits of facial recognition? Benefits include enhanced security, faster identification processes, and improved user convenience in various applications.
- What are the privacy concerns associated with facial recognition? Privacy concerns include unauthorized surveillance, potential misuse by authorities, and the risk of biased outcomes against certain demographics.
- Is facial recognition technology accurate? While it has improved significantly, accuracy can vary based on factors like lighting, angle, and demographic characteristics.

Biometrics in Everyday Life
Biometric systems have seamlessly integrated into our daily routines, transforming how we interact with technology and enhancing our security. Imagine waking up in the morning, reaching for your smartphone, and simply glancing at the screen to unlock it. This is the magic of biometrics at work! From smartphones to security systems in buildings, biometric technologies are not just a trend; they are becoming a fundamental part of our lives.
One of the most significant advantages of biometric systems is their ability to provide a convenient and secure way to authenticate our identities. Let’s take a closer look at some of the ways biometrics are enhancing our everyday experiences:
- Smartphones: Most modern smartphones come equipped with biometric authentication methods such as fingerprint sensors and facial recognition. This technology not only makes it easier to unlock devices but also adds an extra layer of security for personal data.
- Smart Home Devices: Many smart home devices now utilize biometrics to enhance security. Whether it’s a smart lock that recognizes your fingerprint or a home assistant that responds to your voice, these systems make our lives more convenient while keeping our homes safe.
- Financial Transactions: Banks and financial institutions are increasingly adopting biometric authentication for transactions. This means you can authorize payments simply by scanning your fingerprint or using facial recognition, making banking not only easier but also more secure.
Moreover, the incorporation of biometric systems in public spaces has revolutionized security measures. Airports, for instance, are now using facial recognition technology to expedite check-ins and enhance passenger safety. This not only reduces waiting times but also helps authorities identify potential security threats swiftly.
However, while the benefits are substantial, it’s essential to address the concerns surrounding privacy. As we embrace these technologies, questions about how our biometric data is stored and used are becoming increasingly pertinent. Are we trading our privacy for convenience? This is a debate that society must engage in as we move forward.
In summary, biometrics are making our lives easier and more secure, but they also require us to be vigilant about our privacy. As these technologies evolve, so too must our understanding of their implications. Will we continue to embrace biometrics as a standard part of our lives, or will we push back against the potential risks? Only time will tell.
What are biometrics?
Biometrics refers to the measurement and statistical analysis of people's unique physical and behavioral characteristics. This includes technologies such as fingerprint recognition, facial recognition, iris scanning, and voice recognition.
How do biometric systems enhance security?
Biometric systems enhance security by providing a reliable way to verify identities, making it more difficult for unauthorized individuals to gain access to sensitive information or secure areas.
Are there privacy concerns with biometric technology?
Yes, there are privacy concerns regarding how biometric data is collected, stored, and used. It's crucial for individuals and organizations to ensure that biometric data is handled securely and ethically.
What are some common applications of biometrics in everyday life?
Common applications of biometrics include unlocking smartphones, accessing secure facilities, authorizing financial transactions, and enhancing security in public spaces like airports.

Applications in Mobile Devices
In today's fast-paced world, mobile devices have become an extension of ourselves, and security is a top priority. Biometric authentication has emerged as a game-changing feature that not only enhances security but also provides unparalleled convenience. Imagine unlocking your phone just by glancing at it or placing your finger on a sensor—no more fumbling for passwords or PINs! This is the magic of biometrics, and it’s revolutionizing how we interact with our devices.
Smartphones and tablets commonly utilize several biometric methods, including fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, and even iris scanning. These technologies are designed to provide a seamless user experience while ensuring that unauthorized users are kept at bay. For instance, fingerprint scanners are now integrated into the home button or the screen itself, allowing users to unlock their devices effortlessly. On the other hand, facial recognition technology uses sophisticated algorithms to map and recognize facial features, making it incredibly difficult for anyone else to gain access.
One of the most significant benefits of these biometric systems in mobile devices is their ability to enhance user privacy. Since biometric data is unique to each individual, it offers a higher level of security compared to traditional passwords, which can be guessed or stolen. Furthermore, many devices store biometric data locally rather than on cloud servers, reducing the risk of data breaches. However, it's essential to acknowledge that while biometric systems are generally secure, they are not infallible. Users must remain vigilant against potential vulnerabilities, such as spoofing attacks where someone might use a photo or a mold of a fingerprint to gain unauthorized access.
As we look toward the future, the integration of biometrics in mobile devices is expected to become even more sophisticated. For example, advancements in machine learning could lead to improved accuracy in recognizing users, even in varying lighting conditions or angles. Additionally, we may see the emergence of multi-modal biometric systems that combine different types of biometric data—like combining facial recognition with voice recognition—to create an even more secure authentication process.
In conclusion, the applications of biometric technology in mobile devices are not just about enhancing security; they are also about providing a smoother, more intuitive user experience. As these technologies continue to evolve, we can expect even greater innovations that will redefine how we interact with our devices while keeping our personal information safe.
- What is biometric authentication?
Biometric authentication is a security process that relies on unique biological characteristics, such as fingerprints or facial features, to verify an individual's identity. - Is biometric data safe?
While biometric data is generally more secure than traditional passwords, it is essential to ensure that it is stored and processed securely to prevent unauthorized access. - Can biometric systems be fooled?
Yes, biometric systems can be vulnerable to spoofing attacks, where an unauthorized user attempts to gain access using a fake fingerprint or photo. However, advancements in technology are continually improving their security.

Impact on Public Safety
Biometric technologies are reshaping the landscape of public safety in ways that were once considered the stuff of science fiction. Imagine walking down a busy street, and a camera discreetly scans your face, identifying potential threats before they even have a chance to act. This is not just a futuristic dream; it’s a reality that many cities are embracing. With the integration of biometric systems into law enforcement and surveillance, the potential for enhancing safety is immense, but it also raises significant ethical questions.
One of the primary benefits of using biometrics in public safety is the ability to quickly identify individuals in real-time. For instance, facial recognition technology can be utilized in crowded places like airports, stadiums, and public events to monitor for known criminals or missing persons. This proactive approach can lead to quicker responses and potentially prevent crimes before they occur. In fact, studies have shown that cities employing advanced biometric surveillance systems have seen a marked decrease in crime rates, making them safer for residents and visitors alike.
However, while the advantages are clear, the implementation of biometric technologies also comes with a set of challenges. Privacy concerns loom large, as many citizens are uncomfortable with the idea of being constantly monitored. The line between safety and surveillance can become blurred, leading to debates about civil liberties. For example, a recent survey indicated that 70% of respondents expressed concerns about how their biometric data would be used and stored. This highlights the need for transparent policies and regulations governing the use of such technologies.
Moreover, the effectiveness of biometric systems can be influenced by various factors, including environmental conditions and the quality of the technology itself. For instance, poor lighting can affect facial recognition accuracy, while dirty fingerprint scanners can lead to failed identifications. This inconsistency can undermine public trust in these systems, making it crucial for law enforcement agencies to continuously improve and adapt their technologies.
As we look to the future, the role of biometrics in public safety is expected to grow even more significant. Innovations in artificial intelligence and machine learning are paving the way for smarter, more efficient biometric systems. Imagine a world where law enforcement can leverage predictive analytics to anticipate criminal activity based on biometric data patterns. However, with these advancements come even greater responsibilities to ensure that the balance between security and privacy is maintained.
In conclusion, while the impact of biometric technologies on public safety is undeniably positive in many aspects, it also requires a careful and thoughtful approach. As society continues to embrace these innovations, it’s essential to foster a dialogue about the ethical implications and to establish robust frameworks that protect individual rights while enhancing public safety.
- What are biometric technologies? Biometric technologies are systems that use unique physical or behavioral characteristics, such as fingerprints or facial recognition, to identify individuals.
- How do biometric systems enhance public safety? They allow for quick identification of individuals, which can help prevent crime and enhance law enforcement efforts.
- Are there privacy concerns associated with biometric technologies? Yes, many people are concerned about constant surveillance and how their biometric data is used and stored.
- What are some challenges faced by biometric systems? Challenges include accuracy in various conditions, potential misuse of data, and maintaining public trust.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are biometrics?
Biometrics refers to the measurement and statistical analysis of unique physical and behavioral characteristics of individuals. It includes various technologies that recognize these traits for identification and security purposes.
- What types of biometric systems are commonly used?
Common types of biometric systems include fingerprint recognition, facial recognition, iris scanning, and voice recognition. Each system has its own functionality and applications in enhancing security across different sectors.
- How does fingerprint recognition work?
Fingerprint recognition works by capturing the unique patterns of ridges and valleys on an individual's fingertip. This data is then converted into a digital format and compared against stored fingerprints for identification or authentication.
- What are the advantages of using fingerprint technology?
Fingerprint technology offers high accuracy, ease of use, and quick authentication. It's widely used in various environments, from personal devices like smartphones to secure facilities, providing a reliable method for access control.
- What challenges does fingerprint recognition face?
Despite its effectiveness, fingerprint recognition can encounter challenges such as false positives, where the system incorrectly identifies a fingerprint, and the potential for spoofing, where fake fingerprints are used to gain unauthorized access.
- How does facial recognition technology work?
Facial recognition technology analyzes the unique features of a person's face, such as the distance between the eyes, the shape of the jawline, and other characteristics. This data is then used to match and identify individuals in various applications.
- Where are biometric systems used in everyday life?
Biometric systems are integrated into everyday life through smartphones, security systems in buildings, and even in public safety measures. They enhance security and convenience, allowing for easier access while maintaining high security standards.
- What is the impact of biometrics on public safety?
Biometric technologies significantly enhance public safety by improving surveillance and law enforcement capabilities. However, they also raise ethical concerns regarding privacy and the potential misuse of personal data.



















